
HalfPower Points YouTube
Half Power Bandwidth. The half power bandwidth of this radiation is defined by the frequencies where the magnitude of the surface impedance is equal to the impedance of free space:[29]iωL1−ω2LC=ηWe solve for λ to yield the frequencies of the two bandedges:[30]ω2=1LC+12η2C2±1ηC1LC+14η2C2The terms in 1/η2C2 are typically small compared to the terms in 1/LC, so we neglect them to.

PowerPoint Slide Divided Into Four Sections Tutorial YouTube
The half-power point is the angle off boresight at which the antenna gain first falls to half power (approximately -3 dB) from the peak. The angle between the -3 dB points is known as the half-power beam width (or simply beam width ). Beamwidth is usually but not always expressed in degrees and for the horizontal plane.

1 APERTURE EFFICIENCY, HALFPOWER POINT, AND SIDELOBES FOR DIFFERENT... Download Table
The half-power point is the point at which the output power has dropped to half of its peak value; that is, at a level of approximately -3 dB. In filters, optical filters, and electronic amplifiers, the half-power point is also known as half-power bandwidth and is a commonly used definition for the cutoff frequency. In the characterization of.

A À3dB half power point. Download Scientific Diagram
5.2.3 The Half-Power Frequency. The half-power frequency is considered the most important parameter in the filter design as the bandwidth of any filter is related to the half-power frequency. The half-power frequency can be obtained as following ( Soltan et al., 2014 ): Given the values of a, b, α, and β, the value of the half-power frequency.

Gaming Half Powerpoint Template Powerpoint templates, Good presentation, Brand guidelines
The gain-bandwidth product is the region, after the half-power point or full-power bandwidth, where you see a steady, constant decline in the gain of the op amp as the frequency increases. You can calculate the gain-bandwidth product by the formula: Gain-bandwidth Product= Gain x Frequency. Beyond the half-power point frequency, the gain falls.
How to Make a Semi Circle in PowerPoint
The -3dB point of an amplifier is called the half-power point which is -3dB down from maximum, taking 0dB as the maximum output value. Introduction to the Amplifier Example No1. Determine the Voltage, Current and Power Gain of an amplifier that has an input signal of 1mA at 10mV and a corresponding output signal of 10mA at 1V.
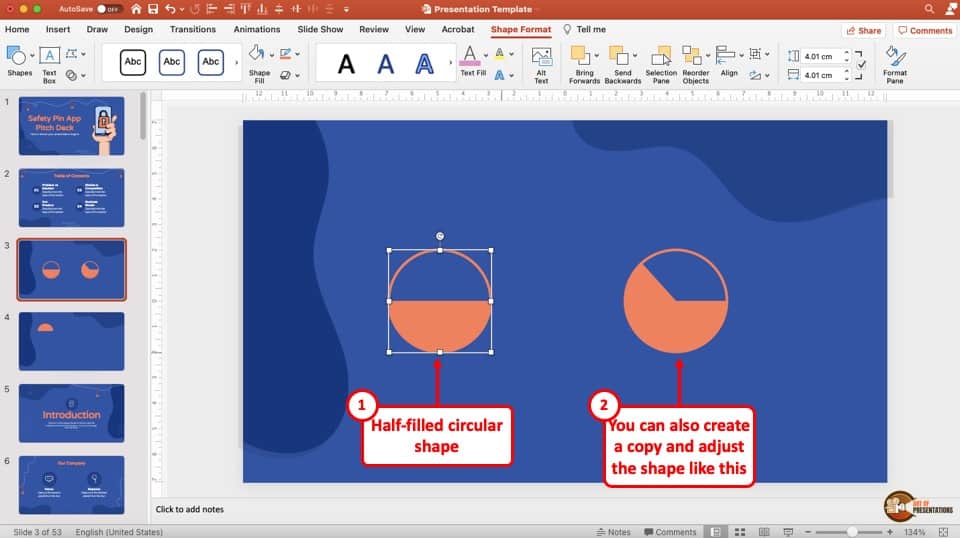
How to Create a SemiCircle in PowerPoint? [The EASY Way!] Art of Presentations
The half-power point is the point at which the output power has dropped to half of its peak value; that is, at a level of approximately -3 dB. [1] [a] In filters, optical filters, and electronic amplifiers, [2] the half-power point is also known as half-power bandwidth and is a commonly used definition for the cutoff frequency.
One Circle Two Half PowerPoint Template PPT Slides
The half-power point is the point at which the output power has dropped to half of its peak value; that is, at a level of approximately -3 dB. [1] [lower-alpha 1] In filters, optical filters, and electronic amplifiers, [2] the half-power point is also known as half-power bandwidth and is a commonly used definition for the cutoff frequency.

PPT PN Junction Devices PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID404842
Half-Power Point. The half-power point or half-power bandwidth is the frequency at which the output power has dropped to half of its peak value; that is, at a level of approximately -3 dB. The half-power point is a commonly-used definition for the cutoff frequency and can be used in a variety of contexts, including the characterization of filters, optical filters, electronic amplifiers and.

Response curve showing bandwidth at halfpower point. Download Scientific Diagram
Half-Power Point. The half-power point or half-power bandwidth is the frequency at which the output power has dropped to half of its peak value; that is, at a level of approximately -3 dB. The half-power point is a commonly-used definition for the cutoff frequency and can be used in a variety of contexts, including the characterization of filters, optical filters, electronic amplifiers and.
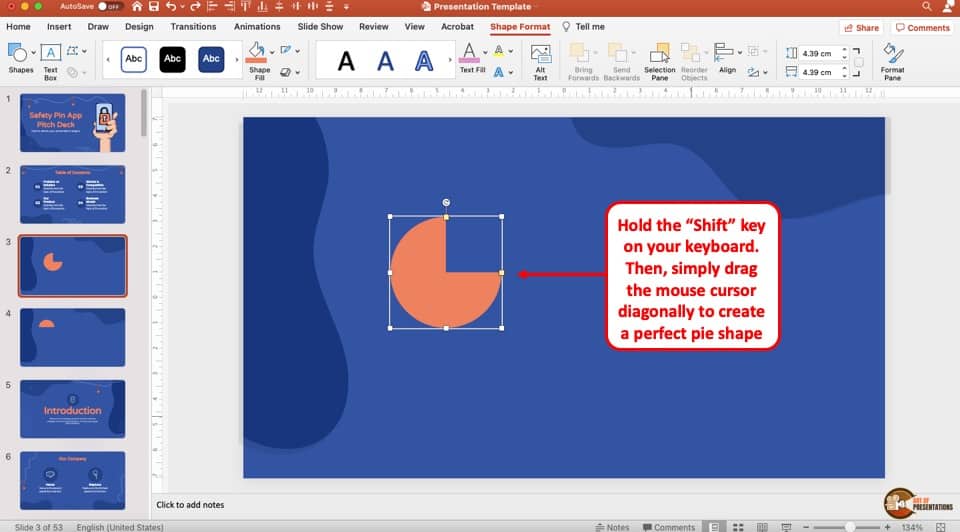
How to Create a SemiCircle in PowerPoint? [The EASY Way!] Art of Presentations
For calculating half power frequency, they set it equal to $\cfrac{1}{2}$ (which I think is the max. value at $\omega = 0$. Can anyone please explain why this difference in solving the problems? Thanks. homework-and-exercises; electric-circuits; electrical-resistance; capacitance; frequency; Share.

HalfPower Point and the 3dB Point. Are they the same? YouTube
The frequencies for which current in a series RLC (or a series tuned) circuit is equal to 1/√2 (i.e. 70.71%) of the maximum current (current at resonance)are known as Half Power Frequencies. At the half power frequencies RMS power consumed by the circuit can be computed by the relation. P = I 2 * R. = (I 0 /√2) 2 * R = P 0 /2 where, P 0.

Toppr Ask Question
2.69K subscribers Subscribe 3K views 2 years ago EPP In this video, we explore the Half-Power Point and the -3dB point. Are they the same? How do we apply them to a Filter Design? We reimagined.
Damping from measurement Part 2 Half Power Points Simulations Machine Dynamics LUT
Complete answer: Half power points frequencies for a given LCR are the frequencies for which the power in the circuit is half of the maximum power in the circuit. The current in the circuit at maximum power is also maximum. Let it be imax. Maximum current is obtained at resonance.

[TUTORIAL] Create a HALF CIRCLE in PowerPoint EASILY (Without Full Outline) YouTube
1. In a pulse, such as an electronic pulse or an optical pulse, one of the pair of points at which the power level is one-half of the maximum or peak level, one point occurring on the leading edge and the other on the trailing edge. 2.

HalfPowerPoint Angle, Beam Crosssection Area and Flux as a Function... Download Scientific
The -3 dB points are also referred to as the half power points on the transfer magnitude curve. Equation (2) is useful for determining the Q values for a multi-degree-of-freedom system as long as the modal frequencies are well separated. Single-degree-of-freedom System Example Consider the single-degree-of-freedom system in Figure 1. x m k c